It's been a year since I wrote about Weird web pages as a prospective catalyst for the reclamation of my digital identity. There's been significant progress towards that end – more spread out among individual efforts than I initially envisioned, but ultimately for the better.
In this time a lot of necessary groundwork has been completed, some of which I didn't even realize was needed until I learned about it. Continuing from where I left off a year ago, let's go a few levels deeper into the vision of Weird, and the more clear-sighted vantage point we're looking out from today.
Starting with the self
Around a month ago I edited Assembling Community OS to reflect an emerging piece of technology which greatly helped crystallize my idea of Weird's most elementary purpose as a product. We'll come back to the shiny tech later; here's what we wanna do with it:
Digital autonomy begets individual freedom begets fairness & equality.
The hopeful possibility of this moment lies in the open-social web protocols which make up the foundations of a comms & coordination ecosystem owned and operated by the general public.
We have yet to bring these components together into one cohesive communications product, wherein messages and knowledge artifacts can move seamlessly from one flow-mode to the next and your identity remains the same throughout. Yet this ideal is closer to becoming reified than you might think.
Here's how I intend to do it, with a lot of help from my friends.
Part 1: Weird Identity
Before I can interact with other netizens, I need an online persona to make my digital self presentable and increasingly trustworthy. That's what Weird is all about. Most basically it's an open source equivalent to Linktree, supercharged by self-sovereign identity.
Weird will aggregate your fragmented persona into a single unified view. Establish your little slice of home on the internet without getting stuck in the content-production imperative of a custom website or a blog.
Then, thanks to the commodification of ID-tech steered by the OIDC standard, Weird can grow up to become a full-fledged identity provider by standing on the sturdy shoulders of rauthy. Meaning, you can 'Login with Weird' and use it as a kind of Gravatar on steroids. This will enable seamless login to all of the additional services we want to plug into our community stack.
To free ourselves of our current predicament, we must simultaneously de-centralize and re-centralize identity.
By de-centralizing the ownership of identity away from platform monopolies and back to individuals, we can re-centralize the agency of personhood.
Once more for clarity:
- Decentralize ownership.
- Recentralize agency.
The central authority of ones digital identity must first and foremost be the individual themselves. That's how we regain our digital sovereignty.
Everything we're gonna build towards in this article is based on The Path to Self-Sovereign Identity by Christopher Allen, written in 2016.
Rather than just advocating that users be at the center of the identity process, self-sovereign identity requires that users be the rulers of their own identity.
This is a lot to take in, so let's unpack it with a practical example.
The unbearable monopolization of being
In order to easily sign up for a new internet service today, without doing the tired email-and-password dance, I use “social sign-in”. We're all familiar with the usual “Google / Facebook / Apple / Microsoft / etc.” options.

It's very convenient because in this glorious age (/s) of technofeudalism you will inevitably have been forced on to one or more of these platforms already. You may as well entrench your identity in their unchallenged dominion even further by accepting their superstructure as the parent authority of that smaller service, even though the two are completely unrelated.
Incidentally, in a fairer world, that small service would be an up-and-coming challenger to the dominance of the ruling platforms. But that game has been rigged for a long time.
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/08/permanent-overlords/
The authors of the paper 'Coopting Disruption: Has Big Tech disrupted disruption itself?' propose a four-step program for the would-be Tech Baron hoping to defend their turf from disruption.
First, gather information about startups that might develop disruptive technologies and steer them away from competing with you, by investing in them or partnering with them.
Second, cut off any would-be competitor's supply of resources they need to develop a disruptive product that challenges your own.
Third, convince the government to pass regulations that big, established companies can comply with but that are business-killing challenges for small competitors.
Finally, buy up any company that resists your steering, succeeds despite your resource war, and escapes the compliance moats of regulation that favors incumbents.
Then: kill those companies.
The authors proceed to show that all four tactics are in play today. Big Tech companies operate their own VC funds, which means they get a look at every promising company in the field, even if they don't want to invest in them. Big Tech companies are also awash in money and their “rival” VCs know it, and so financial VCs and Big Tech collude to fund potential disruptors and then sell them to Big Tech companies as “aqui-hires” that see the disruption neutralized.
Identity feudalism is an invaluable weapon in a tech baron's anti-disruption arsenal. Not only does it provide them with a to-the-second ticker on emergent platform upstarts that show signs of exponential growth, but every smaller player that defers to the mega-platforms for their network effects is consequently helping the fiefdoms deepen their moats by foregoing any network strength of their own.
How corporate centralization begets identity fragmentation
Ironically, the more corporation-centralized our identities become, the more fragmented they actually get. That's because when each of these mega-monopolies are big enough, they consider themselves the ultimate, unparalleled authority of digital identity. You won't find a “Log in with Google” button on Facebook, Apple or Microsoft's account page.
And yet you'll invariably need more than one of these accounts because, much to their chagrin, none of these companies have achieved complete world dominion quite yet. But if we stay the course, it won't be long until we can all enjoy the supreme technoutopian state of Absolute Customer Convenience.
Chain me up and sign me in your lordship!
Additionally, niche-targeted services will ask you to log in via the comparatively smaller but still monopolistic overlords of their particular domain. A project management app for instance might provide social logins via Notion, Slack and GitHub.
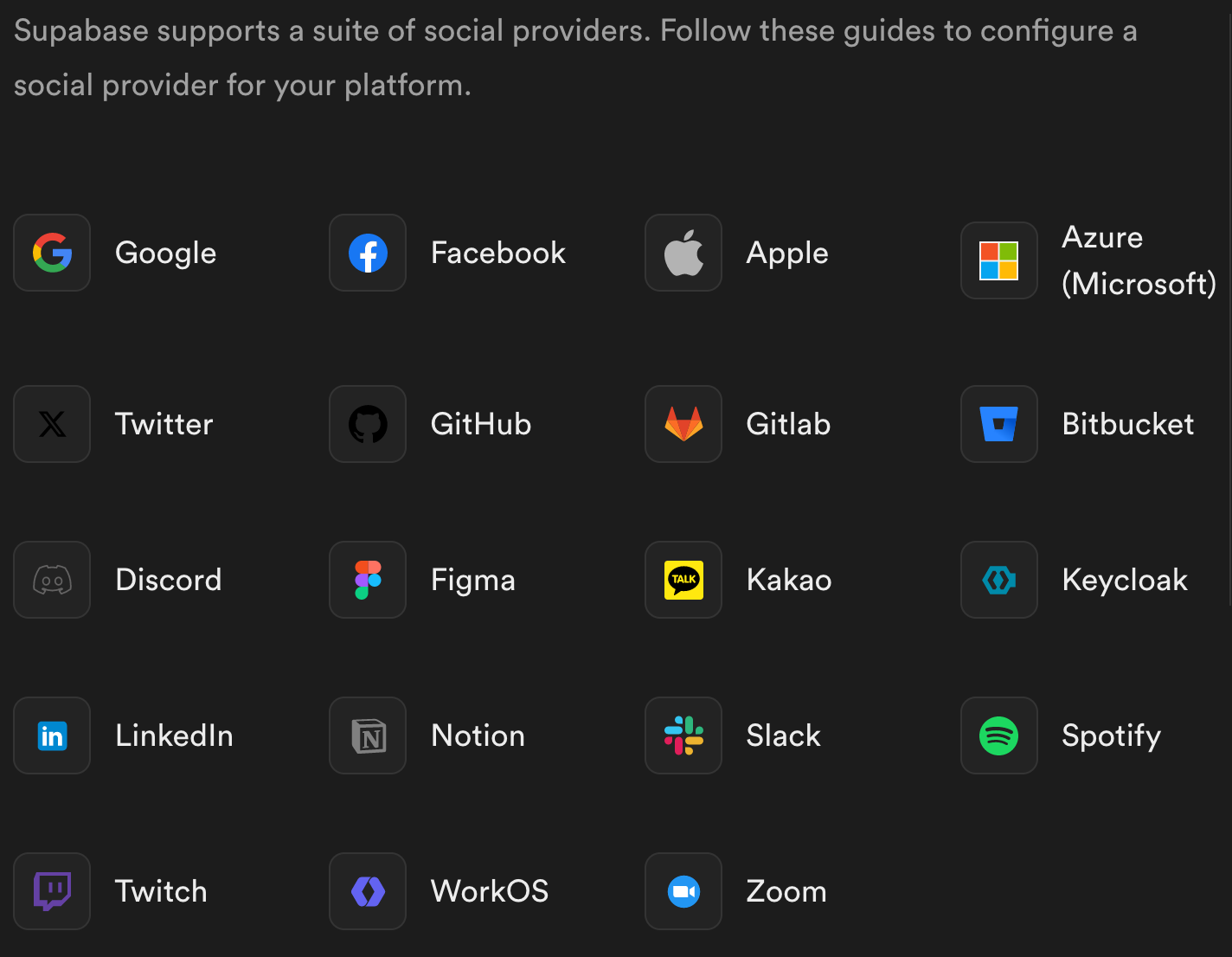
The built-in social providers of the app development platform Supabase demonstrates how fragmented our digitial identities really are in the current landscape:
Decoupling identity
Weird attempts something that other platforms don’t dare to do: It presents identity as the main attraction of its platform offering.
All mainstream identity providers get you hooked into their ID-network by means of a tight coupling between a light identity layer plus a heavy service:
- GitHub: ID + git
- Discord: ID + chat
- Gmail: ID + email
The indivisibility of this coupling weakens our digital sovereignty. Even if I stopped using Gmail for email, I still rely heavily on it for my authentication to hundreds of sites & services. It’s part of their lock-in scheme.
Gmail et.al. make identity confusing because they've made it appear necessarily coupled with an overarching complexity like email or a social network. But identity should stand on its own. In fact it is paramount that our identity is not owned by a personal-data-loving megacorp because there's nothing more valuable for them to keep locked up than the very essence of your digital self.
However, identity on its own just doesn't sell because we've become complacently accustomed to it as a byproduct of a headliner service, and usually a “free” one at that.
So Weird makes a compromise. We acknowledge that plain identity is somewhat lackluster, at least in the current landscape. To be competitive, we loosely pair your identity with what is arguably the other side of the identity coin anyhow: The personal webpage.
- Weird: ID as dynamic API + ID as static page.
And a ‘linkspage’ is the lightest, most low-effort webpage there is, since it only requires you to add links to wherever your online identity is already fragmented to.
Identity tech
Time for the techy bits! The past year has brought a series of innovations that, if brought together into a cohesive product such as Weird and others, could truly rock the foundations of the identity oligopolies.
I desperately want to be set free from my Big ID dependence. Sadly that cannot happen overnight since most sites need to explicitly add additional login options. Yet, a lot can happen sooner rather than later in the IndieWeb and fediverse that I now spend most of my online hours in.
Most of those web apps don't provide any 'social' login at all, but they absolutely should for the sake of easier onboarding. They just need better options than the mega platforms they are actively trying to avoid.
This and more is becoming possible thanks to three loosely related developments that are maturing simultaneously:
Commodified identity providers – OIDC libs
Federated logins – Bring Your Own Identity Provider with FedCM
Portability – Decentralized identity standards
As I map out these technologies, I'll also outline a rudimentary product plan for Weird as an identity provider for the IndieWeb. By the end it should be clear that Weird hopes to be one among many providers of such a service. That's how we collectively wrest back independent control of the web's identity infrastructure.
Commodified OIDC
It wasn't long ago that aspirations of being a root identity provider was reserved for large and mostly closed-source companies. Now this space is rife with open source solutions backed by single-vendor cloud companies or industry coalitions:
Keycloak has been around forever. In the Supabase-logins example above, Keycloak stands out as the only open source option in the whole bunch.
Weird aims to appear on such lists as well. We keep our stack as lean as possible though, which boiled our search down to the perfect match I mentioned at the top of this article: Rauthy.
A Rauthy deployment with the embedded SQLite, filled caches and a small set of clients and users configured typically only uses between 17 and 22 MB of memory!
Rauthy's tiny footprint means we can realistically offer Weird as a self-hosted product for anyone who doesn't want to rely on our cloud service. In this first section however we'll focus on Weird as a cloud platform.
Now let's imagine what it would take to have 'Login with Weird' show up as an alternative on a real production service. For example, I'm an avid user of the read-it-later app Omnivore. Their login page currently looks like this:

With any of the closed incumbents it's practically impossible to advocate for a new login option that isn't a “trustworthy” trillion dollar company. But Omnivore is open source, which opens up a vastly different possibility space.
Quite simply, our advocacy would start with a Pull Request that implements Weird Login. Maybe we'd start it off as a humble text-button above “Continue with Email”, and continue proving our merits as a first-tier login option from there. That's where the linksapp component comes in as a way to build trust by brand recognition.
Still, this is only a very partial solution to the problem before us.
Firstly, there's a significant burden involved, both upon us to send out a bunch of PRs to services we'd like to make friends with as well as the maintainers who need to review, merge & service said PRs.
Secondly, this type of integration doesn't work for self-hosters. You can't send a PR to Omnivore requesting that they add a dedicated button for 'Login with Andy's site' (for Andy's use only), alongside hundreds of others.
That brings us to the next piece of the puzzle..
Federated social logins
Two months ago, a developer put out a call-to-action regarding the emerging FedCM standard:
FedCM is a method that allows users to log into websites through federated identity services, such as “Sign in with…”, without sharing personal information with either the identity service or the website.
In short, FedCM makes it possible for the identity service of choice to be determined client-side in the browser, instead of that choice having already been made for you server-side, as with the examples of Supabase and Omnivore above.
It's 'Bring Your Own Identity Provider' (BYOIDP), meaning Andy can opt to 'Login with Andy's site' without Omnivore having any prior knowledge of Andy's site and its capability as an identity provider. Or, if Andy doesn't want to self-host their own provider, 'Login with Weird'.
However, true free-for-all user choice is only a tentative part of this WIP specification, and could get retracted in favor of a far more limited selection of The Usual Suspects if no practical example of the former is brought forth.
Fellow internet activist Julian Foad picked up on this movement and echoed the call with a more pointed reiteration of what's at stake. A challenge has been put to the open source community by the drafters of FedCM: Either implement a real-world example of the free-for-all method, or consider your inaction a vote for business as usual.
Three weeks ago one of the former editors of the spec completed the missing piece in the browser for the whole flow to be tested end-to-end.
Ok, I finally got this merged in chrome canaries, so I think we now have a complete prototype of this API in chrome canaries for you all to try.
We need developers to try this API in chrome canaries and give us validation that this is a problem worth solving (and that the proposal actually meets the requirements – or make a counter proposal), so that we can move into more stable channels (next step is an origin trial). Developers do that by writing prototypes that use the API.
If we don't hear from developers, we'll at some point delete the prototype: no specific deadline, just being transparent that the way to move this forward is for developers to build prototypes too (not blog posts, not manifestos: code, counter-proposals or questions).
Weeks passed without anyone apparently answering the call, so I finally decided to take what little action I could on my own. I reached out to sjud who had been experimenting with Rauthy in his personal projects for a bit, and he has graciously agreed to explore this work as part of a modest sponsorship arrangement.
Follow along here: https://github.com/sebadob/rauthy/discussions/145#discussioncomment-8831943
Once we have this working, that's a massive step towards re-centralizing identity around the individual. We're still one crucial step shy of making our identities properly self-sovereign however.
Portable Identities
Here's another excerpt from Christopher Allen's foundational article:
Self-sovereign identity is the next step beyond user-centric identity and that means it begins at the same place: the user must be central to the administration of identity. That requires not just the interoperability of a user’s identity across multiple locations, with the user’s consent, but also true user control of that digital identity, creating user autonomy. To accomplish this, a self-sovereign identity must be transportable; it can’t be locked down to one site or locale.
The Verge recently interviewed Bluesky CEO Jay Graber. When asked what distinguishes Bluesky's ATprotocol from prior art such as ActivityPub, Jay pointed to account portability as a major motivation for a whole new protocol:
Then another thing was we really wanted to get account portability. So, this ability to leave with your identity and your data and have fallbacks with the way that we’ve designed your repo, you can even back up all your posts on your phone or back it up on your server that you control, and then you don’t have to have any sort of friction when you want to move.
So, you can move between services in ActivityPub. But if… for example, Queer.af recently, their .af domain was seized by Afghanistan, and then people were stuck because there was no warning, and then they have to rely on their old server to help forward their stuff over to a new place. So, we wanted to get around that problem and make sure people always had the ability to move.
They're building A Self-Authenticating Social Protocol, which comes with a form of portable identity.
Many people in the ActivityPub-based fediverse consider Bluesky an affront to their pre-existing community; a threat even. I'm not really on the Bluesky network in any meaningful capacity, but I'm glad to have them around because they present a live counterfactual to the ActivityPub story. I don’t think we’d be talking as much and pushing as hard for things like nomadic identity if it hadn’t been for Bluesky championing that feature as one of their key differentiators.
In spite of its largely volunteer-driven development team, the fediverse isn't far behind on The Path to Decentralized Identity in ActivityPub.
So where does Weird come into this? Well, even a portable identity needs a place to live. The self-hosting types will want sole custody of their identity keys, storing them locally on an encrypted drive.
That doesn't work for me. If I had ever gotten into crypto, I'd no doubt be the guy desperately looking for his lost hard drive in a junkyard. I'm messy; I do not trust myself to take proper care of something that will have irrevocable consequences if I lose it.
Bluesky recognizes this as well, which is why they are building a hybrid solution wherein a server host (like Bluesky themselves) and an end-user share non-exclusive custodianship of an identity key.
While I agree that there’s every reason to be cautious about Bluesky’s centralized approach, I think it’s worth noting that private-key identities solve two distinct problems:
Instance-independent identity with credible exit
Self-sovereign identity with no 3rd party authority
As already explained, personally I don’t actually want to be 100% responsible for the safeguarding of my private identity key, for the same reason I use a bank instead of storing my money in a safe at home.
I want to fully own my identity, but I don’t need exclusive custodianship over it. I have a much more urgent need for (1) than (2), so I’m okay with solving the former first as long as there’s a clear path from there to the latter.
Bluesky’s approach is in principle fine with me, provided the promise of credible exit can be substantiated. My main concern with Bluesky Inc. specifically is that they're a VC-funded ($8m seed) company with >30 employees and no concrete business plan. With that many people on the payroll the money is gonna go quick, so I'll be very surprised if they don't do another funding round in the next 6-12 months, thus sinking them even deeper into VC debt.
I'm not fundamentally against venture capital, but by now we have a lot of historical proof that the more of it you take on, the more compromised your original vision gets.
https://waxy.org/2024/01/the-quiet-death-of-ellos-big-dreams/
Despite their idealist manifesto and their Bill of Rights, I don’t believe they could ever truly be in partnership with their community once they were taking large amounts of venture funding. All of their ideals and big dreams were easily undone, even the legal restrictions they defined in their Public Benefit Corporation charter:
Ello made money from selling ads to third parties;
Ello made money selling their user data to a third party;
Ello was sold, and the new owners didn’t comply with those terms.
I might only be willing to trust an external identity custodian if it was Mozilla or some other similarly established open-web institution.
Or, hear me out, maybe such a custodian wouldn't have to meet the high bar of longstanding open-internet staple as long as it is sufficiently lean, transparent and indie-oriented. Like, say, Weird!
Here's where another magic property of the OIDC standard (as implemented by Rauthy) comes into play: it provides a baseline of ID management for other, still experimental methods to plug into.
For instance, Rauthy already supports Solid OIDC, enabling interoperability with the Solid protocol as yet another alternative for decentralized identity, or just as a means of integrated key storage.
Bluesky is also working on OAuth support (with some talk of OIDC compatibility).
Bluesky wants to be “the last social identity you’ll ever have to create”. It's a nice sentiment, but I think it's a bit like trying to sell “the last jacket you'll ever wear”.
I think the real mark of a truly user-respecting identity provider is one that is equally happy to be your primary or secondary provider, and can operate as one or the other interchangeably.
Furthermore, ones identity can never be tied down to just one thing. In the timeless words of Walt Whitman, “I am large, I contain multitudes”.
Just so, an identity container made to last forever must be built to hold an ever changing number of multiple personas.
Let's try to make that shall we? Join us in #weird on Matrix.